[Collaborative Article] | Employing Chemical Proteomics Strategy to Unveil the Target Protein Network of Cisplatin and Enhance Understanding of its Anti-Cancer Mechanism
With the rapid advancements in modern medicine, significant breakthroughs have been achieved in cancer drug research and development. Among these, cisplatin stands out for its potent anti-tumor efficacy in treating various solid tumors, serving as a beacon of hope for numerous cancer patients. Despite its widespread clinical use, understanding the internal mechanisms of cisplatin's action remains a central topic actively pursued by the scientific community. In this context, a research team from Tongji College of Pharmacy, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, has published an article titled "Molecular Targets of Cisplatin in HeLa Cells Explored Through Competitive Activity-Based Protein Profiling Strategy" in the Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry (Impact Factor 3.9). Leveraging Competitive Chemical Proteomic Analysis Technology based on cysteine-specific probes (Competitive ABPP), the study accurately identifies cisplatin targets and their sites of action in HeLa cells.

With the rapid advancements in modern medicine, significant breakthroughs have been achieved in cancer drug research and development. Among these, cisplatin stands out for its potent anti-tumor efficacy in treating various solid tumors, serving as a beacon of hope for numerous cancer patients. Despite its widespread clinical use, understanding the internal mechanisms of cisplatin's action remains a central topic actively pursued by the scientific community. In this context, a research team from Tongji College of Pharmacy, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, has published an article titled "Molecular Targets of Cisplatin in HeLa Cells Explored Through Competitive Activity-Based Protein Profiling Strategy" in the Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry (Impact Factor 3.9). Leveraging Competitive Chemical Proteomic Analysis Technology based on cysteine-specific probes (Competitive ABPP), the study accurately identifies cisplatin targets and their sites of action in HeLa cells.
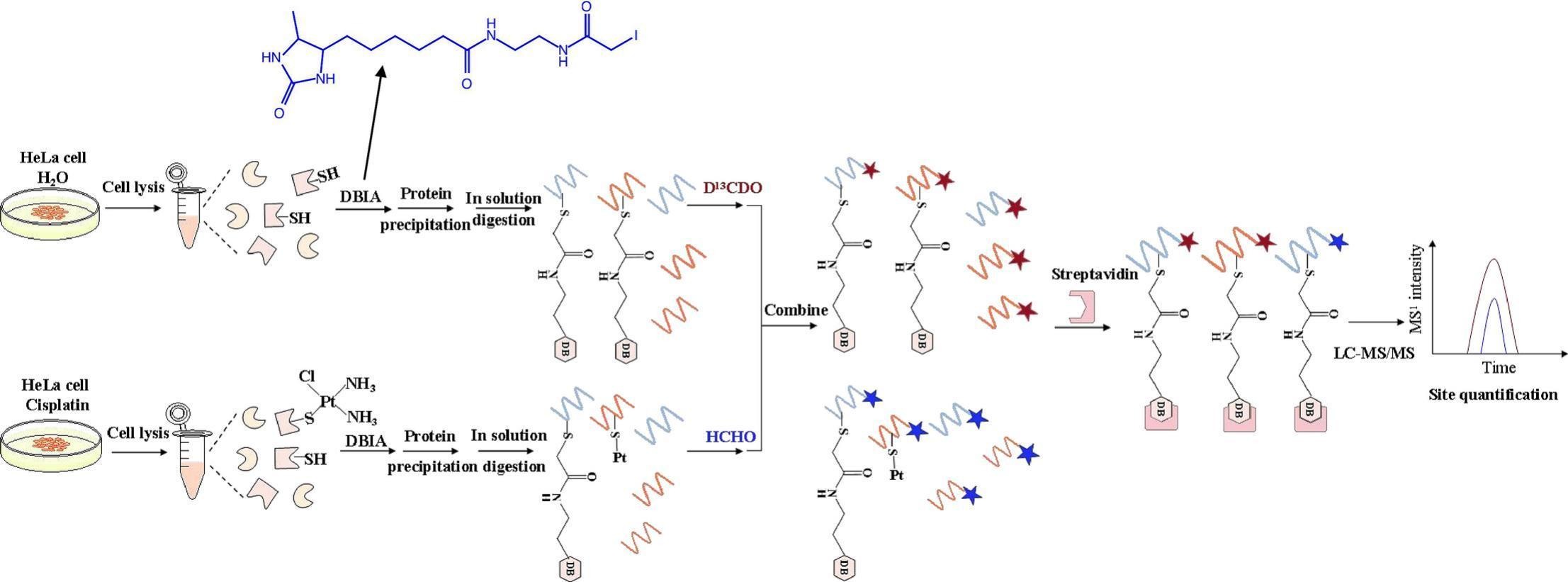
A competitive cysteine profiling method was used to identify cisplatin-binding cysteine in HeLa cell proteomes using the desthiobiotin iodoacetamide probe.
In this article, Chomix provided expert support in chemical proteomics sample preparation and mass spectrometry identification and analysis during the target discovery process. Leveraging high-resolution mass spectrometry equipment and chemical proteomics technology, cisplatin-treated HeLa cell samples underwent a series of analyses including cysteine-reactive probe (DBI) labeling, protein precipitation separation, trypsin digestion, isotope labeling, enrichment of probe-labeled peptides, and LC-MS/MS. This comprehensive approach successfully identified 3571 peptides, corresponding to 1871 proteins, with 46 proteins identified as potential targets of cisplatin. These target proteins are predominantly associated with folate metabolism, protein deubiquitination, tetrahydrobiopterin synthesis, tetrahydrofolate metabolism, and other pathways. Chomix's professional target identification service ensures the reliability and accuracy of data, significantly enhancing the credibility and scientific value of the research results.
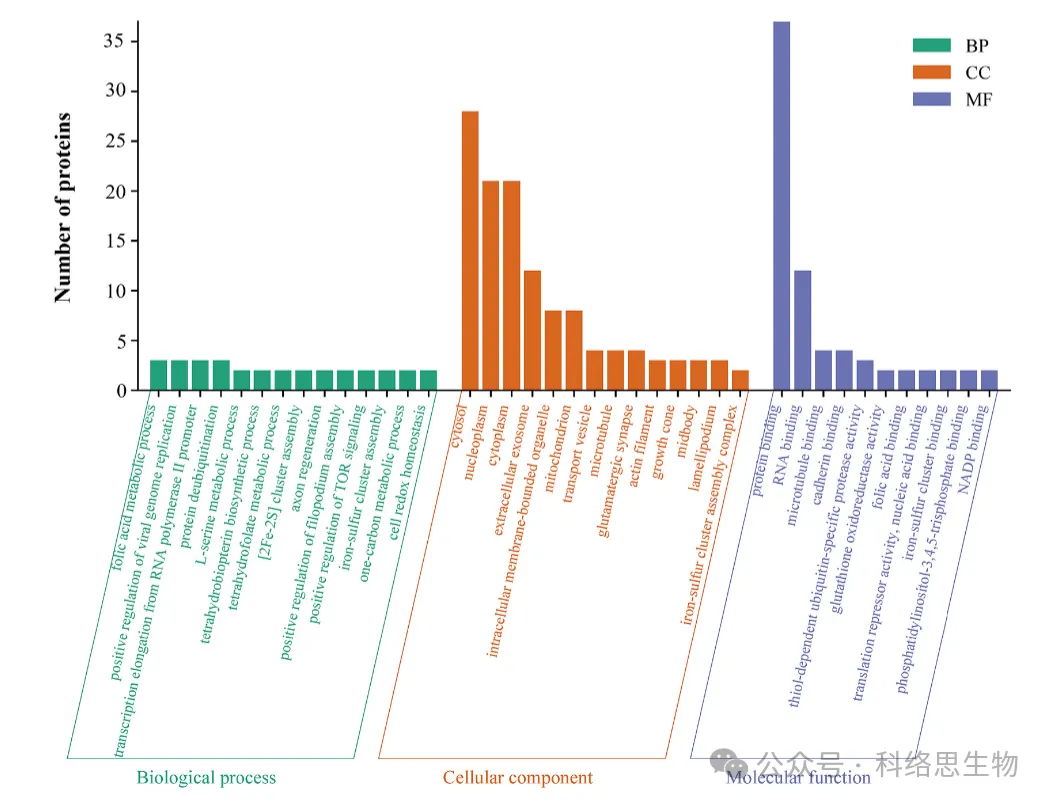
Figure 2: Functional Analysis of Cisplatin Target Proteins
In addition to chemical proteomics sample preparation and mass spectrometry identification, the target identification services provided by Chomix also include the identification of drug-protein binding sites, which is crucial for revealing the mechanism of action of drugs. To further validate the binding effect between cisplatin and its newly discovered protein targets, the high-confidence CAPN 1 was chosen for validation. The protein was incubated with cisplatin at a molar ratio of 1:10, and a new product peak was observed in addition to the original mass peak of the protein, with the mass difference matching that of 10 cisplatin molecules. This result clearly demonstrates the interaction between CAPN 1 and cisplatin. Previous studies have shown that cisplatin-induced apoptosis in HeLa cells is inhibited, indicating a positive correlation between the protein and the anti-tumor activity of cisplatin. This study provides new insights to further explore the mechanism of action and toxicity of cisplatin.
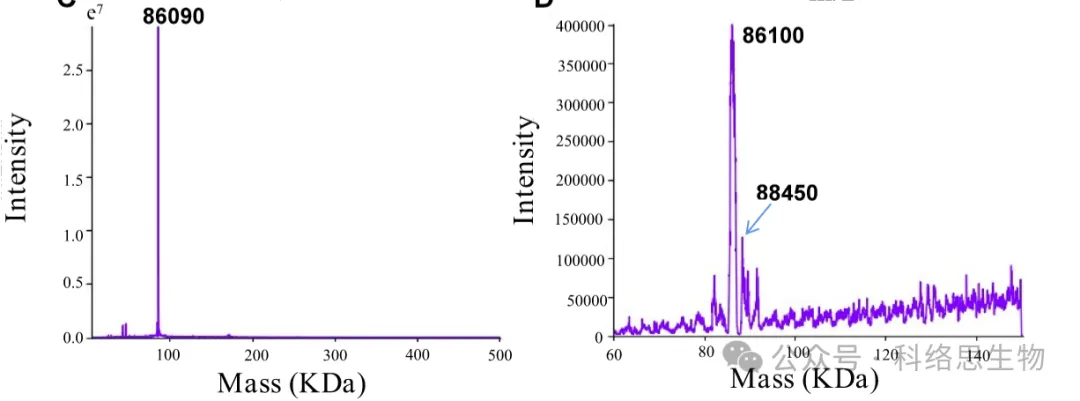
Figure 3: Before and After Reaction between CAPN 1 Protein and Cisplatin.
In summary, this article successfully elucidates the targets of cisplatin in HeLa cells using the Competitive ABPP method, identifying the novel target CAPN 1. This discovery provides crucial insights into the mechanisms underlying the action and toxicity of cisplatin. Not only does this study enrich our understanding of cisplatin's mechanism of action, but it also furnishes a potent tool for future research endeavors in this domain.
Special Note: This article has participated in the "ChomiX Paper Publication Award Program" and has been awarded a generous prize by Chomix. We extend a warm invitation to more researchers to join the "ChomiX Paper Publication Award Program." By acknowledging ChomiX products or services (e.g., "We thank ChomiX Biotech Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China) for its invaluable contribution to our chemical proteomics experiments."), researchers can potentially participate in this incentive program, fostering innovation and facilitating the exchange of research findings. Chomix remains committed to being a steadfast partner in the scientific research community, actively promoting global scientific progress and collaborating on cutting-edge research into drug mechanisms of action. We eagerly anticipate collaborating with more scientific research teams to usher in a new era of scientific discovery.
Reference: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2024.112518.