Información previa
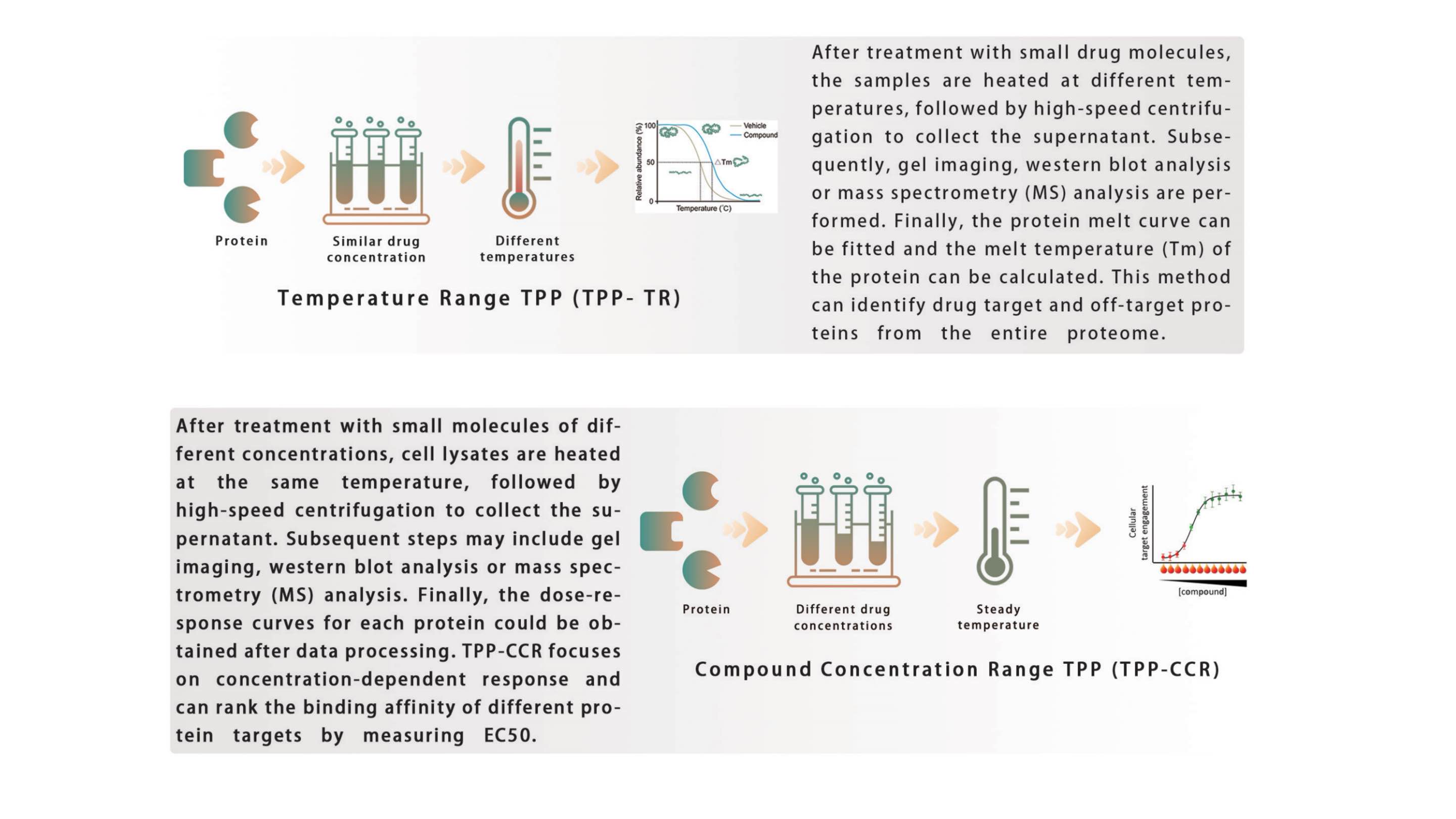
El perfilado de proteoma térmico (TPP) es una técnica que evalúa la estabilidad de las proteínas aplicando calor a células vivas o lisados y analizando los cambios resultantes mediante espectrometría de masas. Al monitorear cómo las proteínas se desnaturalizan y precipitan a temperaturas de fusión específicas (Tm), el TPP ayuda a identificar cómo los fármacos, los ligandos o los factores ambientales influyen en el proteoma. Cuando un fármaco o ligando se une a una proteína, puede alterar la Tm, lo que permite la detección de interacciones fármaco-objetivo. Este enfoque se utiliza ampliamente en el descubrimiento de fármacos y en la proteómica para estudiar la estabilidad, las interacciones y las modificaciones postraduccionales de las proteínas.
Plataforma Técnica
Nuestras ventajas
1. No es necesario modificar las moléculas pequeñas objetivo, evitar cambios en las relaciones estructura-actividad y simplificar el diseño experimental.
2. Aplicable a proteínas puras, lisados (células o tejidos, etc.)
3. Reflejan interacciones directas entre proteínas y moléculas pequeñas.
Estudio de caso
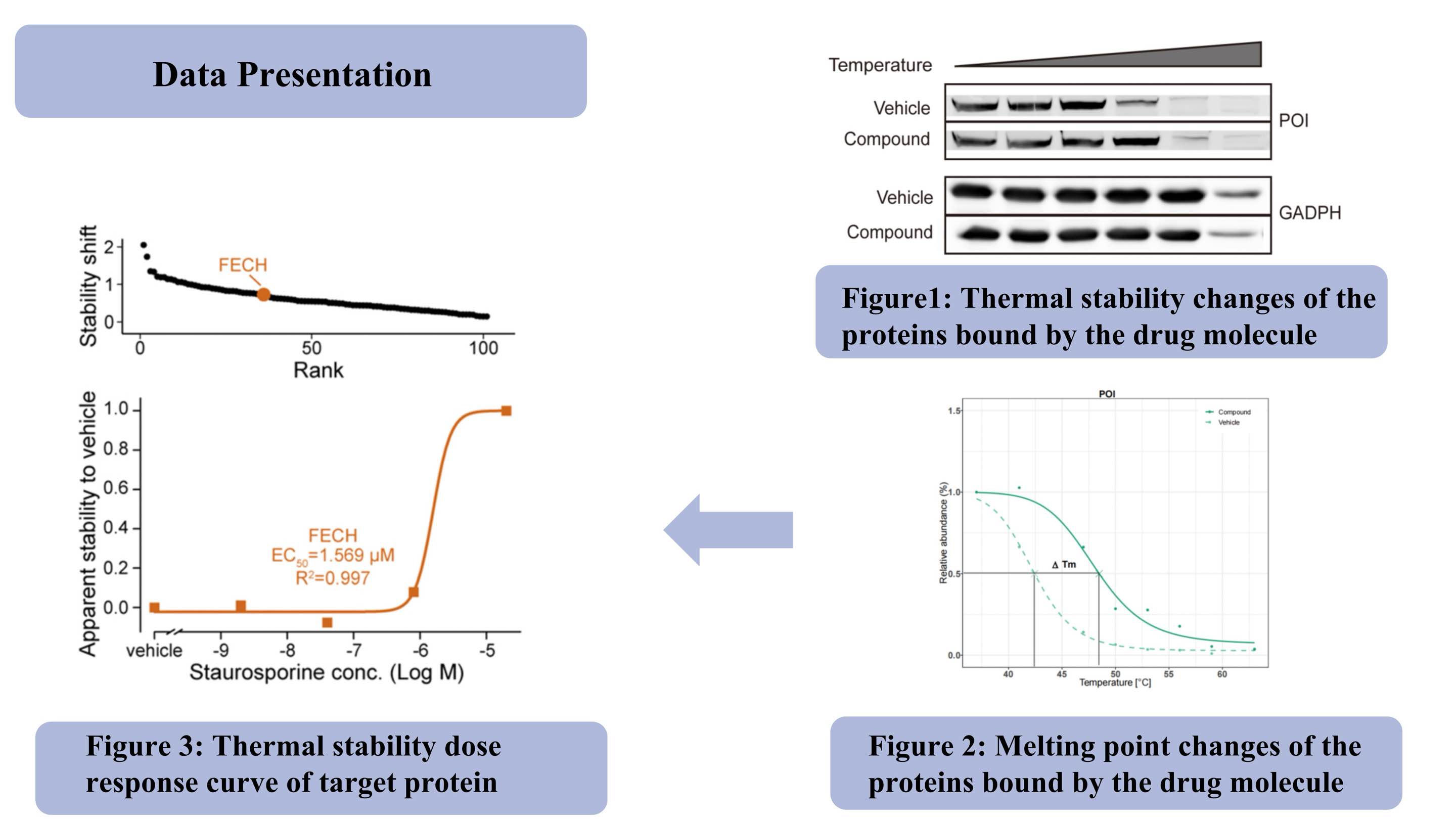
Objetivo del proyecto: verificar si la pequeña molécula objetivo está unida directamente a la proteína objetivo en el lisado celular a través de TPP.
Soluciones: Analice la estabilidad térmica de la proteína objetivo mediante transferencia Western (Figura 1), rango de temperatura TPP-TR (Figura 2) y rango de concentración del compuesto TPP-CCR (Figura 3).