-
Identification of Protein-Protein, Antibody-Antigen Interaction Regions: Chemical Cross-Linking
Identification of Protein-Protein, Antibody-Antigen Interaction Regions: Chemical Cross-Linking Understanding protein structure and interactions is essential for uncovering their biological functions. Due to the proteome’s complexity, no single technique can fully reveal these aspects. Biologists often use a combination of methods, with cross-linking mass spectrometry (XL-MS) standing out for its unique advantages. XL-MS provides precise spatial distance information between amino acid re... -

Identification of Protein-Protein Interaction in Living Cells: Proximity Labeling
Identification of Protein-Protein Interaction in Living Cells: Proximity Labeling Technical Platform The TurboID technology platform involves fusing a mutated biotin ligase to the C-terminus of a target protein. In overexpressed cells, the addition of biotin rapidly biotinylates interacting proteins within 10 minutes, even at room temperature, with minimal background noise. This versatility makes TurboID suitable for a wide range of biological systems, including mammalian cells, pla... -
Protein-Protein Interactions
Protein-Protein Interactions Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) serve as the cornerstone of cellular life activities, playing crucial roles in cell signaling, structural assembly, and key life processes such as pathogen-host recognition. However, many pathological processes are also caused by abnormalities in PPIs. Therefore, intervening and regulating PPIs has shown tremendous potential as a means to treat related diseases. ChomiX integrates a series of cutting-edge technology platform... -
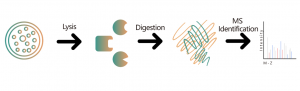
Target Identification and Selectivity Analysis of Targeted Protein Degraders
Target Identification and Selectivity Analysis of Targeted Protein Degraders The Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras (PROTAC) drug is a bifunctional molecule that can bind to the targeted protein and recruit the ubiquitin E3 ligase for degradation. Therefore, novel modalities such as PROTAC and molecular glue have the ability to inadvertently alter the abundance of endogenous proteins, which provides a new therapeutic method for protein targets, especially the undruggable proteins. Comprehensively... -
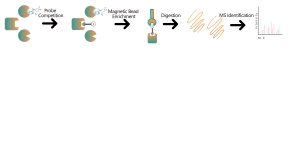
Quantitative Analysis of Occupancy and Selectivity of Covalent Small Molecule Drug Targets
Quantitative Analysis of Occupancy and Selectivity of Covalent Small Molecule Drug Targets Covalent drugs primarily work by forming covalent bonds with specific amino acid residues on target proteins, such as cysteine, lysine, and serine. Aspirin is one of the earliest known covalent drug molecules. Additionally, many natural products exhibit covalent properties, such as oridonin, which has anti-inflammatory bioactivity. In recent years, covalent targeted drugs have gained increasing att... -
Identification of the binding site for non-covalent small molecule drugs in living cells
Identification of the binding site for non-covalent small molecule drugs in living cells At the cellular level, directly studying the mode of action between drugs and target proteins can help avoid changes in protein structure during purification and false-positive results that may arise from artificial buffer systems and high drug-protein concentrations. Technical Platform ChomiX provides chemical proteomics services utilizing biologically active photoreactive chemical probes (with... -
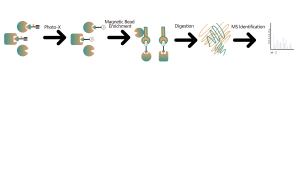
Identification of non-covalent small molecule drug targets based on photoaffinity probes
Identification of non-covalent small molecule drug targets based on photoaffinity probes Technical Platform The chemical proteomics target identification platform based on photoaffinity probes involves several key steps, including probe design, synthesis, activity assessment, labeling, protein enrichment, and data analysis. Non-covalent small molecule drugs, such as synthetic compounds, herbal extracts, natural products, and metabolites, can be modified into photoaffinity probes. On... -
Small Molecule-Protein Interactions
Small Molecule-Protein Interactions Proteins, as the direct participants and executors of life activities, represent crucial targets for disease therapy. Small molecule drugs (organic compounds typically with a molecular weight less than 1000 Da) exert effective therapeutic effects by finely modulating protein activities, abundances, and interactions. Common small molecule drugs include natural products and their derivatives (e.g., herbal monomers) as well as chemically synthesized drugs. Upo... -
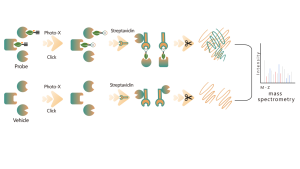
Target Discovery Platform: Unraveling the Mechanisms of Natural Products
The active ingredient within Chinese medicine is a series of compounds that have therapeutic or physiological activities. Chinese medicines are rich in variety, complex in composition, and have a wide range of active ingredients, constituting an important avenue for acquiring active ingredients, lead compounds, and making medicines.
Our chemoproteomics platform excels in discovering protein targets for natural products in Chinese medicine. It ingeniously transforms these natural products into multifunctional chemical probes, mirroring their bioactivities. These probes, when applied within live cells or diseased tissues, can directly capture natural product-binding proteins. With the aid of bioorthogonal coupling reactions, we precisely isolate and enrich these target proteins. Utilizing high resolution mass spectrometry, we achieve pinpoint accuracy down to the binding pockets. It equips us with more comprehensive and accurate information, poised to unveil the intricate mechanism underlying the active ingredients in Chinese medicine.
-
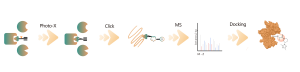
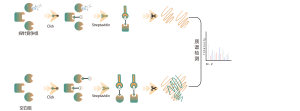
Identification of Non-covalent Small Molecule Binding Pockets in Cells
Identification of Non-covalent Small Molecule Binding Pockets in Cells Platform Technical Features It is critical to determine the binding mode between small molecule drugs and their protein targets for drug R&D. A comprehensive analysis of these interactions at both structural and physico-chemical levels could significantly deepen our understanding of protein functions and facilitate drug design & optimization. Structural biology techniques, including X-ray, cryo-electron microscopy ... -
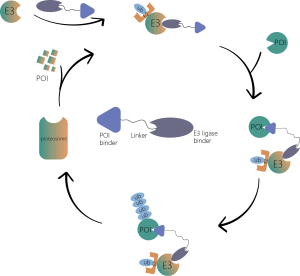
Proteome-wide profiling for Targeted Protein Degradation (TPD) drugs
The Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras (PROTAC) drug is a bifunctional molecule that can bind to the targeted protein and recruit the ubiquitin E3 ligase for degradation. Therefore, novel modalities such as PROTAC and molecular glue have the ability to inadvertently alter the abundance of endogenous proteins, which provides a new therapeutic method for protein targets, especially the undruggable proteins. Comprehensively quantifying the abundance of on and off-target proteins has been one of the standard experiments for TPD drugs R&D.
-
Protein targets identification by differential proteomics
Protein Targets Identification by Differential Proteomics Platform Technical Features Differential proteomics studies the changes of proteome under different physiological or pathological states, such as drug treatments or gene regulation, by comparing two or more samples. This approach sheds light on important life processes or major diseases in order to figure out the key different proteins that are regarded as markers for qualitative and functional analysis. Thousands of proteins can be id...